Google’s new page experience measurements, known as Core Web Vitals, have been incorporated into the Google Search core algorithm as part of Google’s page experience upgrade in 2021, which might have serious ramifications for underperforming websites.
Google created and popularised the notion of Core Web Vitals (CWV) after discovering that consumers prefer and are more likely to convert to on-websites that provide an excellent user experience.
Websites may become better, higher quality search results for Google by using technical SEO that boosts CWV scores—meaning sites with “Good” Core Web Vital scores can earn higher search ranks than sites with “Poor” Core Web Vitals.
The technical elements that determine your website’s Core Web Vitals often need the skills of a senior web developer who understands how to adjust your site at the code level to increase performance and fulfill Google’s page experience benchmarks.
Even if you aren’t a website developer, we can help you grasp these new metrics by simplifying and clarifying the principles underlying each Core Web Vital, as well as investigating why Google values each of them as search signals for page experience.
What Are Google Core Web Vitals?
Google Core Web Vitals are a set of standardized metrics that assist developers in understanding how people interact with a web page. While Core Web Vitals was designed for developers, these tools apply to all site owners since they break down the user’s real-world experience on a page.
Core Web Vitals identifies user experience concerns by creating a statistic for three significant aspects of user experience, which are as follows:
-Performance of page loading
-Interaction simplicity
-The visual stability of a page as viewed by the user
Each of these measures provides a distinct perspective on several characteristics that impact how visitors interact and engage with a website. While developers must consider “user experience” holistically, these independent measurements assist to break down the many elements into smaller parts so that site owners may detect and correct technical faults throughout their website.
It’s crucial to realize that these metrics don’t tell the entire story of a website’s user experience, but each measure may be stitched together to assist engineers to debug effectively and scientifically.
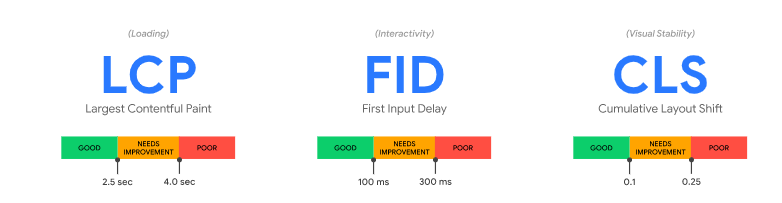
What Are The 3 Core Web Vitals
Let’s look at the three Core Web Vitals to help you optimize your websites right now!
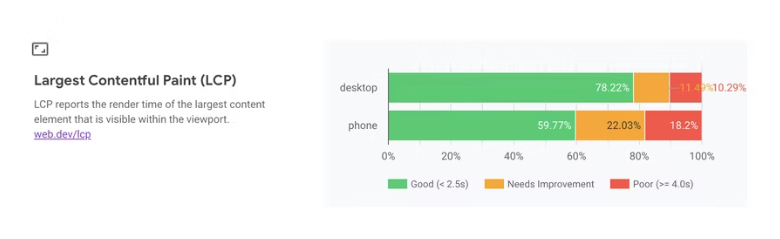
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
The render time of the most significant blocks visible to an audience is a Core Web Vitals measure that site managers may use to analyze the user experience and determine if a user would find a page helpful.
Site owners need their sites to load quickly to provide a satisfying user experience. Load speed is not just important for a great user experience; a website that loads quickly is more likely to rank better on Google.
Furthermore, quick load times have been demonstrated to affect engagement and conversion rates when compared to a website with poor loading times.
What Does LCP Look At?
LCP tracks how long it takes for various content blocks to load into the user viewport (current screen). This rating solely considers how quickly content sections render on the visible screen; nothing below the fold is taken into account.
-Images
-Images from the video poster
-Images for the background
-Text in blocks
To achieve LCP, a page should load in less than 2.5 seconds.
2. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Site owners must make it as simple as possible for visitors to interact with links and buttons on their websites to increase sales and conversions. The cumulative layout move statistic reveals links or buttons that move after a web page has loaded. It shows the number of difficulty visitors will have to engage with features on your site once a page displays.
UX and design are critical components of a successful user experience, and if a web page switches items while a user reads, the user will grow annoyed. Site owners may improve accessibility, increase click-through rates, and increase online sales by using CLS to help developers determine whether images or links have moved on the page.
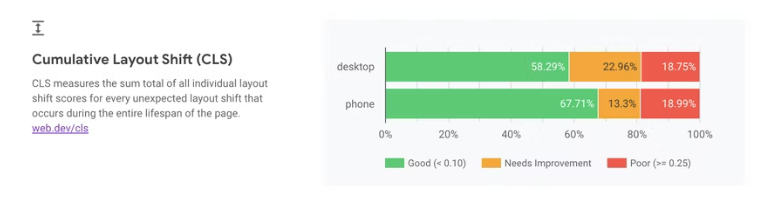
What Does CLS Assess?
CLS regulates whether the location of components in the visible viewport changes between two displayed frames. Simply said, this indicator assists site owners in determining if a material such as text, buttons, and banners are moved about while a user is viewing information on a certain page.
Elements that shift position can confuse visitors and impede their experience on a website, therefore it’s critical to ensure that all information remains in place when a page loads on the user’s device.
CLS examines fundamental parameters to establish the visual stability of a website from the perspective of the viewer, taking various criteria into account:
-Layout modification
-Impact percentage
-Fraction of a distance
Site owners should aim for a CLS of 0.1 or below.
3. First Input Delay (FID)
Online users like pages that are short and easy to navigate. To discover sites that may frustrate your audience, First Input Delay analyses input latency (the time it takes a page element to respond to a user’s input).
To offer material to their viewers, modern websites employ a variety of innovative technologies and dynamic content widgets. While this form of material can increase content delivery, it can also generate delays in which a user must wait for their browser to respond to their input.
To boost engagement and usability across the site, developers must minimize the number of time users spends waiting for a browser to respond to their input.
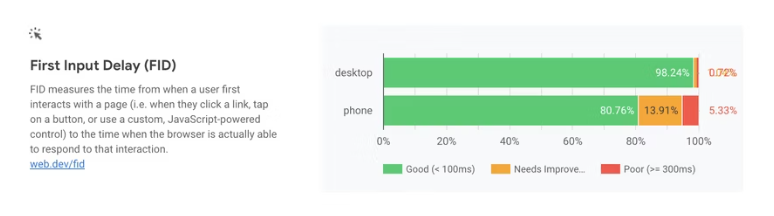
What Does FID Look Like?
FID assesses how responsive a page is when loading user-inputted element inputs. This implies that FID only registers events like key pushes and clicks. . FIDs of under 100 milliseconds should be a goal for website operators that want to provide a good user experience.
It should be noted that FID is difficult to estimate due to its limited availability in the field. This implies that your score will be determined by factors outside your control, such as user device capabilities and Internet speeds as experienced by your audience.
Why Are Core Web Vitals Important For SEO?
Core Web Vitals can assist you in improving your search results. They are significant because they assist Google in determining how well a website works and identifying improvement opportunities.
These measurements, in particular, take into account:
-Loading
-Interactivity
-Visual consistency
These are only a handful of the elements that Google evaluates when determining the health of a website. It also analyses mobile compatibility. This is significant since more individuals are accessing the internet via mobile devices. You might be losing a lot of traffic and income if your website isn’t mobile-friendly.
Another important consideration is website security, which assists you in protecting your site from internet risks such as malware and hackers. It protects both your site’s content and your visitors’ data.
You can enhance your website’s performance and rank better in search results by ensuring that it satisfies certain requirements. To put it another way, prioritizing and improving Core Web Vitals can help you improve your user experience and SEO. This is how Core web vitals affect SEO.
How To Improve Core Web Vitals?
Now that we know what Core Web Vitals are and how they function, we can move on to some best practices. Remember that the particular measures you must do to enhance your scores will be determined by the results of your exam.
As a result, it’s critical to heed PageSpeed Insights‘ comments and recommendations (or other testing tools you use). Here are a few simple techniques to boost your Core Web Vitals score.
1) Render-Blocking Resources Must Be Removed
The static HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files required to render a page on your site are referred to as render-blocking elements. Scripts in each of these files can block your viewers from reading content.
They are often generated by third-party plugins and technologies such as Google Analytics.
However, one technique to keep these scripts from negatively impacting your UX (and so helping to enhance Core Web Vitals) is to remove render-blocking resources and minify and delete any unneeded CSS or scripts.
There are various techniques you may use to do this. One method is to reduce the number of white spaces and superfluous comments in your JavaScript and CSS. By integrating the files, you may reduce your JavaScript and CSS. This is another chore that WP Rocket’s file optimization tool may assist with.

2) JavaScript Loading Should Be Delayed
If you want to improve your FID scores, you may employ a method called delaying JavaScript loading. This is another method for removing render-blocking items.
Because it pauses the download of JavaScript, this method speeds up the loading of your web pages. In other words, rather than waiting for all JavaScript files to load, it loads additional material on the website when a visitor comes.
Your files will be forced to wait until everything else on your web page is ready before loading. You may also tweak your site settings such that the crucial CSS loads ‘above the fold content’ faster. The items on the web page that display initially are referred to as ‘above the fold.’
3) Lazy Loading Should Be Used
We also suggest that you use lazy loading. This helps to guarantee that your pictures load precisely when people arrive at that portion of the web page, rather than loading concurrently with everything else on the page.
Images that load slowly can assist improve your LCP and loading performance.

4) Improve The Fonts On Your Website
The typefaces you choose on your website, like photos, might affect its loading rates. This is because they need the browser to download and load the font family, including all weight variations.
Optimizing your web fonts can assist enhance the speed of your website. This is because optimized web fonts have reduced file sizes and are supplied faster.
A browser may also fail to show text components if the web font associated with them has not yet been loaded. Using fallback fonts, on the other hand, may result in layout adjustments, lowering your CLS score.
We recommend being picky about the typefaces you employ on your website. If you’re using more than two fonts, remove them from individual components and utilize global fonts just to apply the necessary kinds and weights. This ensures that just the fonts necessary for the text are downloaded.
Wrapping up
Hopefully, this post has helped you better grasp what Google’s Core Web Vitals upgrade is all about, as well as the Page Experience Update. It is critical to remember to have a user-centric emphasis when optimizing your website.
Prioritizing user experience is already a start on the right path. You may now begin cleaning up your website and running tests to identify where your trouble areas still exist. Clean up your website by removing extraneous code and plugins that slow down loading and cause delays.
It’s a good idea to evaluate your website’s speed, interactivity, and stability regularly to check if there are any performance concerns. Don’t forget to undertake field data analysis to check how your website performs in real life. If you follow the fundamental principles, your rating will almost certainly improve over time.
- September 17, 2022